|
|
|
 |
| |
Semantic Web |
|
|
| |
The Semantic Web is an extension of the current web in which information has well-defined meaning, where data has abstract representation and is linked to provide more effective discovery, automation, integration, and reuse across various applications.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
The current web is using HTML to specify how to display information on web page for humans to read. Information on the web is searched by the humans, interpreted by the humans, consumed and queried by the humans. In other words, Information is not machine readable and machine understandable. Current web is flooded with the information so searching, extracting, querying, accessing, maintaining and viewing of information is affected].
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
The vision behind Semantic web is to provide knowledge-based web with more meaningful, machine processable information, automated tools and services for accessing, searching, querying, viewing and maintaining information. The realization of Semantic web also helps in B2B and B2C interactions by providing data interoperability and helps to retrieve information from multiple sources. It also provides support for automated negotiation, auctioning, policy and contract management.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
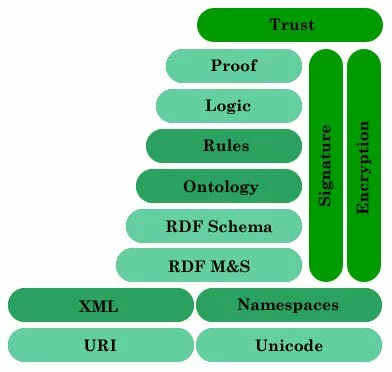
The Semantic Web is built upon XML based standards, languages and tools. The Semantic web uses metadata to provide meaning of the contents. Metadata is data about data. There are three types of metadata syntactic, structural, and semantic]. Metadata add more semantic – meaningful information about the contents. In other words, Semantic web transforms structural information to semantic information.
Many standards have evolved to provide semantic information or to capture the meaning of information and for the realization of Semantic web. W3C has developed XML-based RDF and OWL languages for abstract representation of data, with collaboration from a large number of researchers and practioner. XML allows to create own tags. Tags provide an elemental syntax to add content structure to the documents. It provides no information about meaning of structure or no semantics of the content. XML Schema is restricting the structure and content of XML documents.
|
 |
|
| |
A rule language can be used to query and filter ontology, to infer new knowledge and to make decisions. The rules layer provides simple logic capability. Logic layer provides more advanced logic features. The logic layer enhances the ontology language for writing application-specific declarative knowledge and allows formal logic proofs to be shared. The Proof layer allows representation of proof in the Web language, proof validation and actual deductive process.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Finally, through the use of digital signatures, robust proofs and other knowledge, a trust layer will emerge for application-to-application trust. "Web of trust" is used to indicate the third and final web in Semantic web vision. We will discuss some of the major Semantic web standards such as RDF, OWL and Semantic Web Services standards like OWL-S and WSDL-S which transform Web services to Semantic Web Services and provide automated discovery, composition and execution support.
|
|
 |
|
|
